Double Bond Equivalent or Degree of Unsaturation
The double bond equivalent (DBE) or degree of unsaturation is the rings plus the total number of multiple bonds. DBE is also known as index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD). The double bond equivalent can be calculated by using the formula is given below
Double Bond Equivalent (DBE) = (2C + 2 + N − X − H) / 2
Remember that the presence or absence of oxygen in an organic molecule does not impact the DBE value.
where, C is the number of carbons
N is the number of nitrogens
X is the number of halogens (F, Cl, Br, I)
H is the number of hydrogens
Calculate the degree of unsaturation for benzene.
The molecular formula for benzene is C6H6.
Thus, C = 6, N = 0, X = 0, and H = 6
Substituting the values in the formula we get
Degree of Unsaturation =2(6) + 2 − 6 / 2 = 4
Therefore, Degree of Unsaturation = 4
Calculate the double bond equivalent in glucose.
Molecular formula of glucose is C6H12O6
From formula, DBU = [(2 x 6) + 2 − 12] / 2 = 1
What is the DBE value for lysine?
Molecular formula of lysine is C6H14N2O2
From formula, DBU = [(2 x 6) + 2 + 2 − 14] / 2 = 1
Caculate the double bond equivalent (degree of unsaturation) in compound (A)

H2/Pt causes the catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes. Since 1 mole of the reagent is used, therefore, it will bring about the addition of H2 at one double bond only. So, in the compound A, two cyclopentane rings are should be present along with a double bond. Due to the presence of two rings and one double bond in A its double bond equivalent is 3. We can also calculate it using the formula.
Find the double bond equivalent (DBE) value of the given compound.
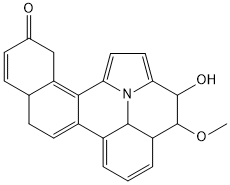
C = 23, H = 21, N = 1, C = 3
Double Bond Equivalent (DBE) = [(2 x 23) + 2 + 1 − 0 − 21] / 2 = 14
Find the double bond equivalent (DBE) value of the given compound.

C = 14, N = 2, O = 3, H = 10
Double Bond Equivalent (DBE) = [(2 x 14) + 2 + 2 − 10] / 2 = 11
Find the double bond equivalent (DBE) value of the given compound.
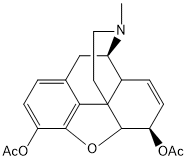
Try to solve
Double Bond Equivalent Calculator
Also read Calculation of π, σ, single and double bonds in Straight Chain and Cycloalkene
