Walden Inversion
Walden inversion is a chemical reaction that reverses the configuration of a chiral center in a molecule. Walden inversion is also known as optical inversion. The reaction is named after Russian, Latvian, and German chemist Paul Walden who discovered it in 1895.
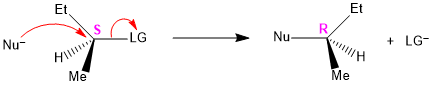
Since a molecule can form two enantiomers around a chiral centre, the Walden inversion converts the configuration of the molecule from one enantiomeric form to another.
In a SN2 reaction, Walden inversion occurs at a tetrahedral carbon atom wherein the leaving group departs and incoming group attached at the same time (concerted process).
Walden inversion can be visualized by imagining an umbrella turned inside-out in a gale.