Osmotic Pressure
When two solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane, there is a spontaneous flow of the solvent from low to high concentration due to osmosis. The pressure that must be applied on the solution of higher concentration to prevent the flow of the solvent from the solution of lower concentration is called osmotic pressure of the solution. It is denoted by π
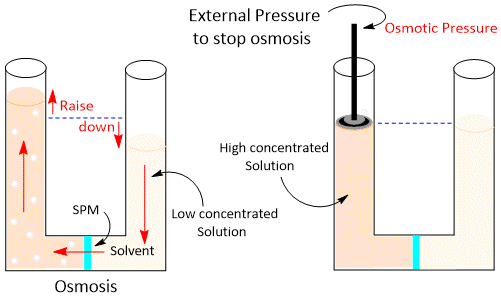
We can determine the Osmotic pressure with the help of the following formula-
π = i × C × R × T
where,
i is van't Hoff factor.
C is molar concentration of the solute in the given solution.
R is universal gas constant.
T is temperature on the Kelvin scale.
